Reducing CO2 footprint with heat pumps
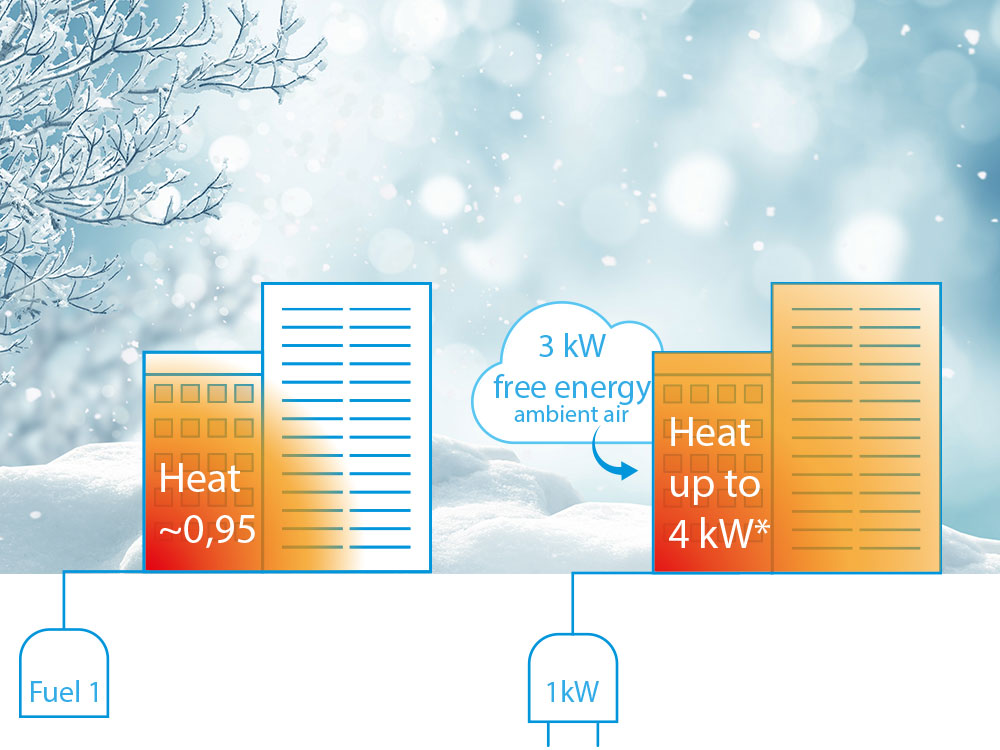
In line with the EU’s "Renovation Wave for Europe", electrifying heat using renewable-powered heat pumps is pivotal for reducing carbon emissions. Traditional boilers have an efficiency of 95%, meaning that 95% of gas energy is converted into useful heat, with 5% of waste heat.
Heat pumps, on the other hand, even in colder environments harness free heat from various sources and transfer it to buildings, utilising electricity. As three-quarters of the energy used for heating comes for free while only consuming a quarter in electricity use, heat pumps are up to four times more efficient than a gas system.
This technology holds great promise in curbing carbon emissions.
Return on Investment
The drive toward heating electrification in line with EU decarbonisation goals and fluctuating energy costs underscores the significance of replacing old gas boilers with advanced heat pump technology. This transition not only aligns with decarbonisation targets but also promises substantial energy savings and swift return on investment (ROI). Swapping out fossil-fuelled boilers for heat pumps or upgrading HVAC systems can deliver notable CO2 reductions, offering an acceptable €/tCO2e ratio and an appealing ROI timeline, for both boiler replacement and new buildings.
The decarbonisation effect
Many companies striving for sustainability share a common objective: reducing CO2 emissions. Achieving this reduction is a known result of the decarbonisation effect stemming from heat pump technology's higher efficiencies and the lower emission factors of electricity grids compared to gas boilers. The impact of this decarbonisation effect is evident when comparing CO2 emissions between the two technologies, with heat pumps substantially outperforming gas boilers: for a process cooling application where a boiler is replaced with a more efficient heat pump solution, ca. 70% of CO2 emission can be reduced.
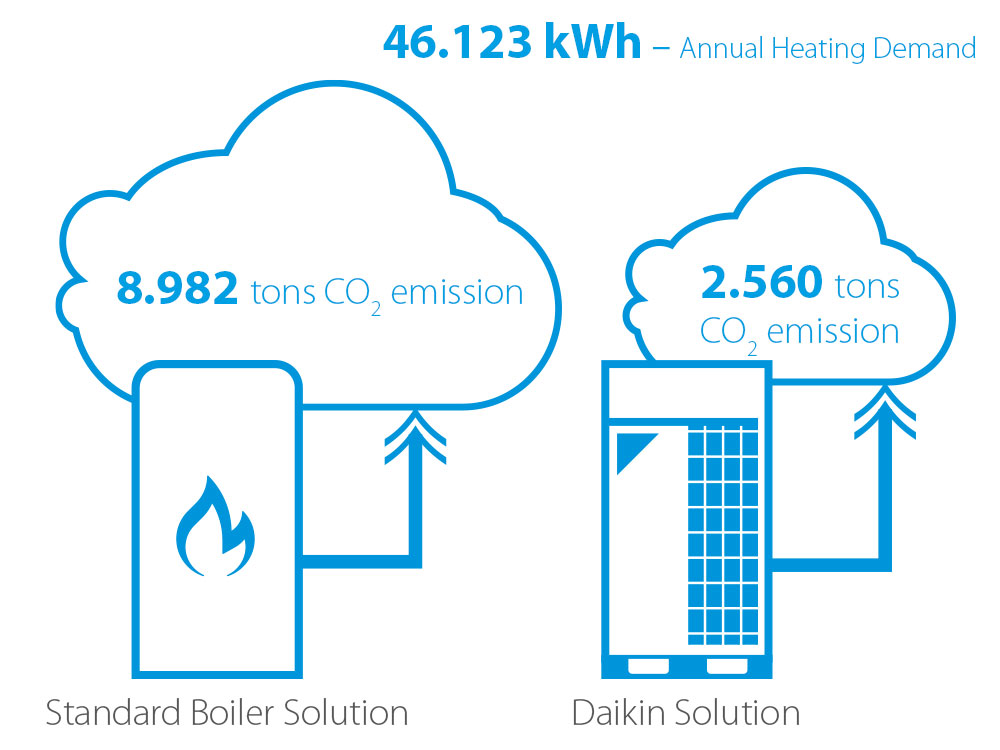
(*) The results shown are valid only for the exact sample project conditions and may vary for each project.
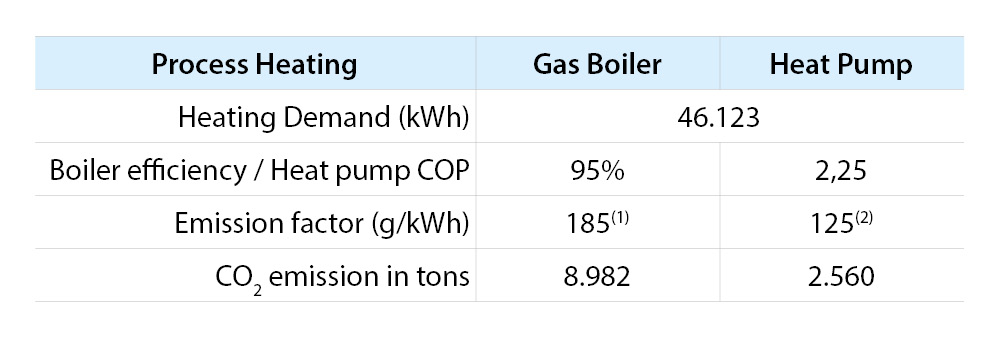
Note: Project life time is considered to be 15 years. The calculation above is based on a 70°C water temperature supply for both boiler and the heat pump.
Find your heat pump
Air-to-Air Heat Pump
Air-to-air heat pumps transfer heat between the building and outdoor air using refrigerant gas providing heating, cooling, and sanitary hot water.
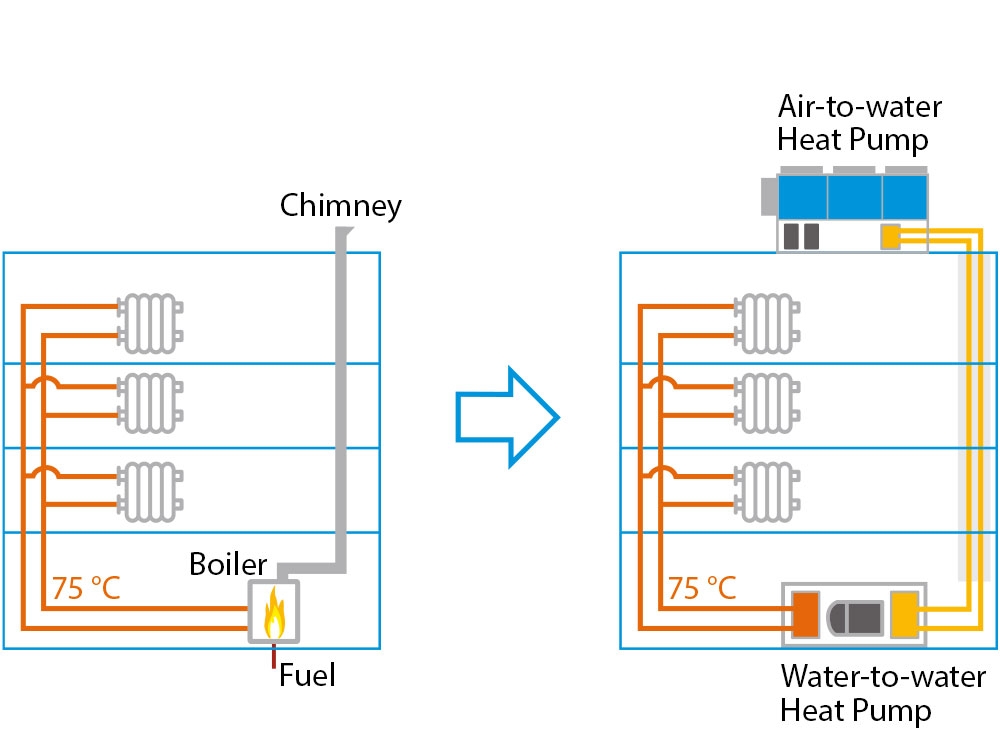
Air-to-Water Heat Pumps
Air-to-water heat pumps transfer heat between the building and outdoor air using refrigerant gas and water, providing heating, cooling, and sanitary hot water.
Water-to-Water Heat Pumps
Water-to-water heat pumps transfer heat between the building and various energy sources using a refrigerant gas and water providing heating, cooling and sanitary hot water.